- Home
- Masterbatch
- Additive Masterbatch
- Anti-Block Masterbatch
- Anti-Fog Masterbatch
- Anti-Microbial Masterbatch
- Anti-Oxidant Masterbatch
- Anti-Static Masterbatch
- Anti-Termite & Rodent Masterbatch
- Desiccant / Anti-Moisture Masterbatch
- Optical Brightener Masterbatch
- Flame Retardant Masterbatch
- Slip Masterbatch
- Polymer Processing Aid (PPA) Masterbatch
- UV Masterbatches
- VCI Additive Masterbatch
- Filler Masterbatch
- Black Masterbatch
- White Masterbatch
- Color Masterbatch
- Mono Masterbatches
- Special Effect Masterbatches
- EVA Masterbatch
- OXO Biodegradable Masterbatch
- XLPE Masterbatch
- Cable Masterbatch
- Nylon Masterbatch
- TPU Masterbatch
- Additive Masterbatch
- Compound
- Market
- Company
- Blog
- Contact Us
Top 5 Cable Compounds: Key Types and Their Applications Explained
Cable compounds play a vital role in modern electrical systems. These specialized materials provide insulation and protection to cables, ensuring efficiency and safety. Various types of cable compounds exist, each with unique properties and applications.
Understanding the key types of cable compounds helps in selecting the right material for specific needs. For instance, thermoplastic and rubber compounds are commonly used. They vary in flexibility, temperature resistance, and durability. Additionally, there are compounds designed for outdoor use and those suited for high-voltage applications.
However, choosing the right cable compound can be challenging. Factors like environmental conditions and mechanical stress need careful consideration. Each compound has its strengths and weaknesses. It is crucial to reflect on these points to avoid costly errors in cable selection and installation.

Overview of Cable Compounds and Their Importance in Industries
Cable compounds play a crucial role in various industries. These materials ensure the safety and efficiency of electric cables. Different environments require specific cable compounds for optimal performance. Without proper materials, cables could fail under stress. This can lead to significant downtime and safety hazards.
Common types include PVC, PE, TPE, and XLPE. Each of these serves distinct needs. For instance, PVC is widely used due to its flexibility and cost-effectiveness. PE offers excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for outdoor applications. TPE is more flexible, suitable for portable cables. XLPE withstands high temperatures and is used in demanding environments.
Yet, not all compounds meet high standards. Some may lack durability, especially under extreme temperatures. This can result in an early cable failure. Industries must carefully choose the right compound. Ignoring this can be costly and dangerous. Analyzing application requirements is key to avoiding potential issues.
Top 5 Cable Compounds: Key Types and Their Applications Explained
| Cable Compound Type | Description | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) | A versatile and cost-effective plastic used in cable insulation. | Good flexibility, moisture resistance, and electrical insulation. | Residential wiring, telecommunications, and automotive applications. |
| XLPE (Cross-Linked Polyethylene) | A high-performance insulation material known for thermal resistance. | High thermal stability, chemical resistance, and excellent electrical properties. | High voltage cables, industrial power systems, and renewable energy systems. |
| LSZH (Low Smoke Zero Halogen) | Designed to emit minimal smoke and toxic fumes when burned. | Low toxicity, low smoke, and high flame resistance. | Public buildings, transportation systems, and areas requiring fire safety. |
| HFFR (Halogen Free Flame Retardant) | Flame-retardant compounds that do not contain halogens. | Flame resistance, mechanical strength, and low smoke emissions. | Telecommunications, power generation, and control systems. |
| EPR (Ethylene Propylene Rubber) | Rubber compound offering excellent heat and oil resistance. | High flexibility, low-temperature performance, and durability. | Submarine cables, mining, and heavy-duty industrial applications. |
Common Types of Cable Compounds and Their Chemical Properties
Cable compounds play a critical role in ensuring the performance and durability of electrical cables. Common materials include PVC, PE, XLPE, and TPE. Each type has unique chemical properties and applications.
PVC is popular due to its versatility. It offers good thermal and mechanical stability. However, it can be less environmentally friendly compared to other options.
Polyethylene (PE) is another widely used compound. It is favored for its excellent electrical insulation properties. PE has a low dielectric constant, making it ideal for high-frequency applications.
XLPE, or cross-linked polyethylene, enhances thermal resistance, making it suitable for underground installations. Yet, it can be more expensive to produce, raising concerns for budget-conscious projects.
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE) are gaining traction as well. They combine flexibility with excellent chemical resistance. Despite their benefits, TPEs can be challenging to process. Industry reports indicate that the demand for advanced cable compounds is rising, projected to grow at a rate of 5.6% annually through 2030. This highlights a shift towards more sustainable and efficient materials in the cable industry, prompting reflection on current practices.
Applications of PVC Cable Compounds in Electrical Wiring
PVC (polyvinyl chloride) cable compounds are widely used in electrical wiring. These compounds offer excellent insulation properties and resistance to moisture. They adapt well to various environments. According to a recent industry report, the global PVC cable market is expected to grow by 4.2% annually. This growth highlights the compound's popularity in residential and commercial installations.
One notable feature of PVC is its flame retardancy. In case of fire, PVC slows down the spread of flames. This quality makes it ideal for safety-critical applications. However, PVC isn't without its challenges. It can emit harmful fumes when burned. Awareness of this issue is essential for manufacturers and users alike.
The flexibility of PVC cable compounds is another advantage. They are easy to install in tight spaces. However, over time, exposure to sunlight can cause PVC to degrade. This raises concerns about long-term durability. As technology evolves, finding better solutions remains a priority for the industry.
Thermoplastic Elastomers: Versatility in Cable Manufacturing
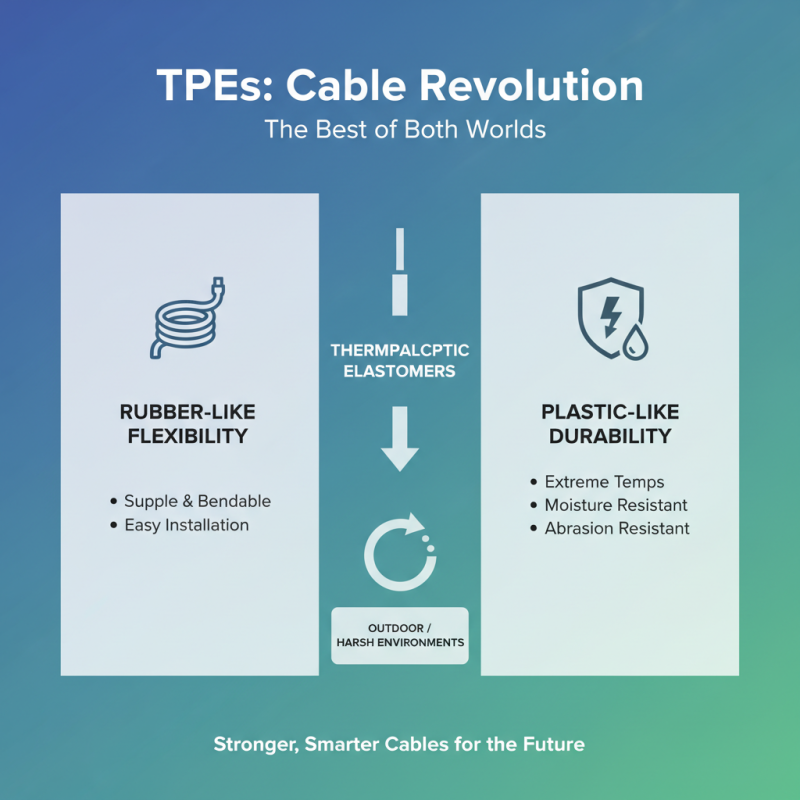
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) are revolutionizing cable manufacturing. These materials combine the best features of rubber and plastic. This unique blend allows for flexibility and durability. TPEs are resistant to various environmental factors. They can withstand extreme temperatures and exposure to moisture. This makes them ideal for outdoor applications.
When cables need to be flexible yet strong, TPEs shine. They can be molded into complex shapes easily. This is key for modern cable designs. Their elasticity helps cables endure repeated bending and twisting. This is crucial in sectors like automotive and electronics. Yet, the production process can lead to inconsistencies. Manufacturers must monitor TPE quality closely.
The versatility of TPEs also extends to insulation. They provide excellent electrical insulation properties. This adds safety to many electrical applications. However, not all TPEs are created equal. Choosing the right type can be challenging. Missteps in selection may lead to underperformance. Each project has unique demands. Understanding TPE characteristics is vital for optimal results.
Performance Comparison of Various Cable Compounds in Real-World Use
When choosing cable compounds, performance in real-world applications is vital. Common materials include PVC, XLPE, TPE, and rubber. Each compound serves different uses, and their performance can vary significantly.
For instance, PVC is widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and decent durability. However, its flexibility can be a challenge in extreme temperatures. In contrast, XLPE offers superior heat resistance and lower dielectric losses. Reports show XLPE cables can handle temperatures up to 90°C, making them ideal for industrial applications.
TPE combines flexibility and strength, crucial in outdoor settings. Rubber compounds often excel in dynamic environments, although they can be heavier and more expensive.
Tips: Always consider the environment where cables will be used. Hot, moist places? Don’t underestimate wear and tear. Regular inspections help catch issues early. Testing various compounds is critical. It allows you to observe their performance under real workloads. There is no one-size-fits-all solution. Each application might reveal unforeseen challenges.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Biodegradable Masterbatch Options for Sustainable Packaging Solutions
-

2025's Top 10 Plastic Filler Masterbatch Innovations for Enhanced Performance
-

What is Color Masterbatch and How It Transforms Plastic Manufacturing
-

Top 10 Benefits of Using Compound Masterbatch in Plastics Manufacturing
-

Exploring the Benefits of Using White Masterbatch in Sustainable Plastic Production
-

Top 5 Surya Masterbatch Options for Enhanced Plastic Performance
