- Home
- Masterbatch
- Additive Masterbatch
- Anti-Block Masterbatch
- Anti-Fog Masterbatch
- Anti-Microbial Masterbatch
- Anti-Oxidant Masterbatch
- Anti-Static Masterbatch
- Anti-Termite & Rodent Masterbatch
- Desiccant / Anti-Moisture Masterbatch
- Optical Brightener Masterbatch
- Flame Retardant Masterbatch
- Slip Masterbatch
- Polymer Processing Aid (PPA) Masterbatch
- UV Masterbatches
- VCI Additive Masterbatch
- Filler Masterbatch
- Black Masterbatch
- White Masterbatch
- Color Masterbatch
- Mono Masterbatches
- Special Effect Masterbatches
- EVA Masterbatch
- OXO Biodegradable Masterbatch
- XLPE Masterbatch
- Cable Masterbatch
- Nylon Masterbatch
- TPU Masterbatch
- Additive Masterbatch
- Compound
- Market
- Company
- Blog
- Contact Us
Understanding Biodegradable Masterbatch: Benefits, Applications, and Innovations
In recent years, the demand for sustainable materials has prompted significant advancements in the field of biodegradable masterbatch. As environmental concerns escalate, particularly regarding plastic waste, the shift towards eco-friendly alternatives has become imperative. According to a report by Smithers Pira, the global biodegradable plastics market is projected to reach 29 million tons by 2024, with a significant portion comprised of biodegradable masterbatch products. This surge is driven by various industries, including packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods, where the need for sustainable solutions is becoming increasingly recognized.
Biodegradable masterbatch serves as a crucial innovation in this landscape, providing a means to enhance the properties of conventional plastics while ensuring an environmentally friendly lifecycle. By incorporating biodegradable polymers into traditional resin matrices, manufacturers can create materials that decompose more rapidly in natural environments, thus reducing the longevity of plastic pollution. The application of biodegradable masterbatch spans diverse sectors, from bioplastics used in food packaging to agricultural films that support soil health and minimize waste. As researchers and companies continue to innovate, the potential for biodegradable masterbatch to revolutionize material science and contribute to a circular economy is profound.

Biodegradable Masterbatch: An Overview of Its Composition and Functionality
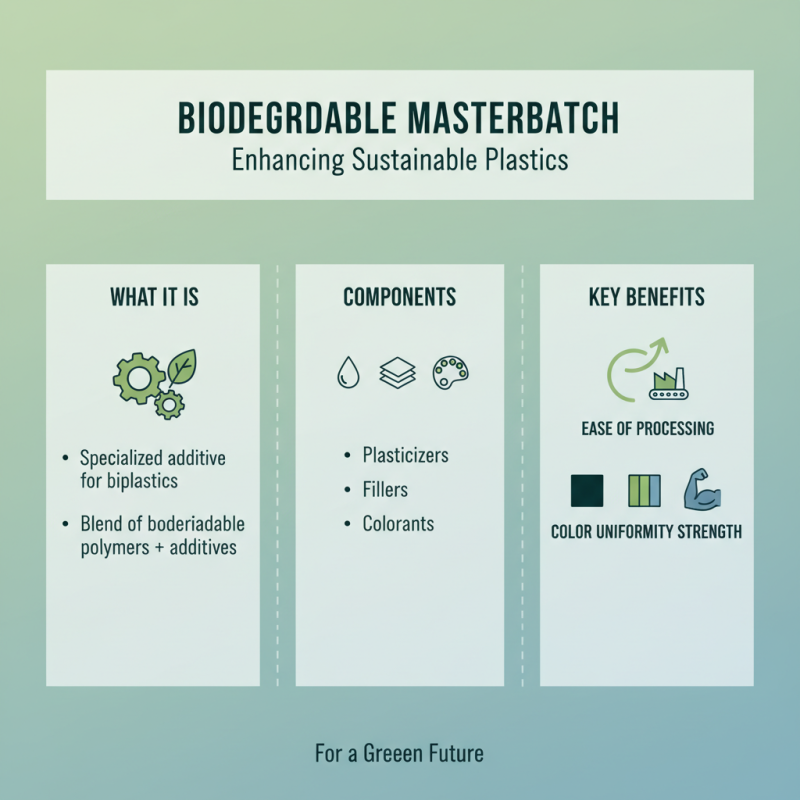
Biodegradable masterbatch is a specialized additive used in the production of biodegradable plastics, enhancing their performance while ensuring environmental responsibility. This masterbatch typically consists of biodegradable polymers combined with several other components such as plasticizers, fillers, and colorants, which contribute to its functionality. The primary aim is to facilitate the processing of biodegradable plastics during manufacturing, providing the necessary characteristics such as ease of processing, color uniformity, and mechanical strength.
In terms of functionality, biodegradable masterbatch plays a vital role in making plastics more versatile and user-friendly. By incorporating biodegradable materials, it allows for a reduction in reliance on conventional plastics, thus addressing pressing environmental concerns. The masterbatch can be engineered to govern degradation rates, offering opportunities for tailored applications in various industries, from packaging to agricultural films. Additionally, innovations in this field continue to evolve, focusing on enhancing the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of biodegradable solutions, making them increasingly viable alternatives in the marketplace.
Key Benefits of Using Biodegradable Masterbatch in Various Industries
Biodegradable masterbatch is becoming increasingly important as industries seek sustainable alternatives to traditional plastic materials. One of the key benefits of using biodegradable masterbatch is its potential to reduce environmental impact. These materials are designed to break down over time, minimizing landfill waste and contributing to a circular economy. By incorporating biodegradable additives, manufacturers can produce products that not only meet consumer demands for sustainability but also comply with stricter environmental regulations.
Another significant advantage is the versatility of biodegradable masterbatch across various applications. From packaging to agriculture, its use can be found in multiple sectors aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. For instance, in the food packaging industry, biodegradable masterbatch allows for the production of compostable bags and containers, enhancing the disposal process without harming the environment.
In agriculture, biodegradable mulch films aid in soil health while eliminating the need for plastic waste removal, demonstrating its functional benefits alongside ecological benefits. As innovations continue to emerge, the potential for biodegradable masterbatch to transform conventional practices becomes even more promising.
Applications of Biodegradable Masterbatch in Packaging and Consumer Goods
Biodegradable masterbatch has emerged as a vital component in the packaging and consumer goods industries, addressing the increasing demand for sustainable materials. By incorporating biodegradable polymers into plastics, manufacturers can enhance their products' environmental profile while maintaining functionality and aesthetic appeal. This innovation allows for the development of packaging solutions that break down naturally over time, reducing landfill waste and minimizing the ecological footprint of everyday items.
In packaging, biodegradable masterbatch contributes to various applications, such as food wrappers, bags, and containers. These materials can decompose in composting environments, promoting a circular economy and supporting the drive towards eco-friendly practices. Consumer goods, including disposable utensils and personal care products, also benefit from this technology. By opting for biodegradable masterbatch, companies can meet consumer preferences for environmentally responsible products while complying with regulatory requirements around plastic usage.
Tips for businesses considering biodegradable masterbatch include assessing the specific application and the environmental conditions it will face during disposal, as these factors can influence the degree of biodegradability. Collaborating with suppliers who specialize in biodegradable materials can also facilitate access to the latest innovations and formulations. Additionally, educating consumers about the benefits of using biodegradable products can enhance brand loyalty and contribute to broader sustainability goals.
Innovations Driving the Future of Biodegradable Masterbatch Technology
The future of biodegradable masterbatch technology is being driven by a wave of innovative practices that aim to enhance the performance and sustainability of plastic products. One significant innovation is the development of biopolymers derived from renewable resources, which can effectively replace traditional petroleum-based materials. These biopolymers not only offer superior biodegradability but also maintain the mechanical properties required for various applications. In addition, advances in additives that accelerate degradation processes are being incorporated into masterbatch formulations, enabling products to break down more quickly and efficiently in natural environments.
Furthermore, research is continuously exploring new processes for the production of biodegradable masterbatch, focusing on reducing energy consumption and waste generation during manufacturing. Techniques such as nanotechnology are being applied to enhance the dispersion of biodegradable fillers, ultimately improving the physical characteristics of the end products. Additionally, innovations in film and coating technologies are expanding the applications of biodegradable masterbatch in packaging, agriculture, and consumer goods, contributing to a circular economy. The integration of these innovations showcases a commitment to sustainability while addressing the growing demand for environmentally friendly materials.
Understanding Biodegradable Masterbatch: Benefits, Applications, and Innovations
| Dimension | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Composition | Biodegradable polymers such as PLA, PBAT, and starch-based materials |
| Benefits | Reduced environmental impact, compliance with regulations, consumer preference for sustainable products |
| Applications | Packaging, agricultural films, disposable cutlery, and food containers |
| Current Innovations | Improved degradation rates, enhanced mechanical properties, integration with recycling technologies |
| Market Trends | Increasing demand for eco-friendly products, collaboration between manufacturers and researchers |
| Challenges | Higher production costs, limited consumer awareness, and disposal infrastructure |
Challenges and Solutions in Implementing Biodegradable Masterbatch

The implementation of biodegradable masterbatch presents several challenges that need to be addressed to maximize its potential in various applications. One significant challenge is the compatibility of biodegradable materials with existing processing technologies. Many manufacturers rely on conventional polymers, and integrating biodegradable options often requires adjustments in machinery and production methods. This can involve substantial investment, which may deter smaller companies from making the switch. Developing masterbatches that can universally blend with different types of polymers without compromising performance is essential to overcome this hurdle.
Another pressing issue is the variability in the degradation rates of biodegradable materials influenced by environmental conditions. Many biodegradable masterbatches are designed to break down under specific settings, such as industrial composting facilities, which are not always accessible. Consequently, there is a need for innovations that ensure a consistent performance regardless of the disposal environment. Research into formulating masterbatches that can degrade efficiently in a variety of conditions, including home composting and marine environments, is crucial for increasing acceptance and usage across industries. Addressing these challenges through collaborative research and development initiatives will foster a more robust integration of biodegradable materials into everyday products.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Biodegradable Masterbatch Options for Sustainable Packaging Solutions
-

Unlocking the Potential of Filler Masterbatch: Innovations in Polymer Manufacturing
-

Unlocking Creativity: How Special Effect Masterbatches Transform Modern Plastics with 30% Enhanced Visual Appeal
-

Exploring the Future of EVA Masterbatch: Trends and Innovations in Polymer Additives for 2024
-

Unlocking the Benefits of Anti Block Masterbatch: Revolutionizing Plastics with Enhanced Performance
-

Top 5 Surya Masterbatch Products to Boost Your Plastic Manufacturing Efficiency
